A Complete Guide on How to Correctly Label the Following Features of the Lymphatic System.
Correctly Label the Following Features of the Lymphatic System.
As an expert in the field, I’ve come across many questions about the lymphatic system and the importance of correctly labeling its features. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of this vital system and explore how each component plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health.
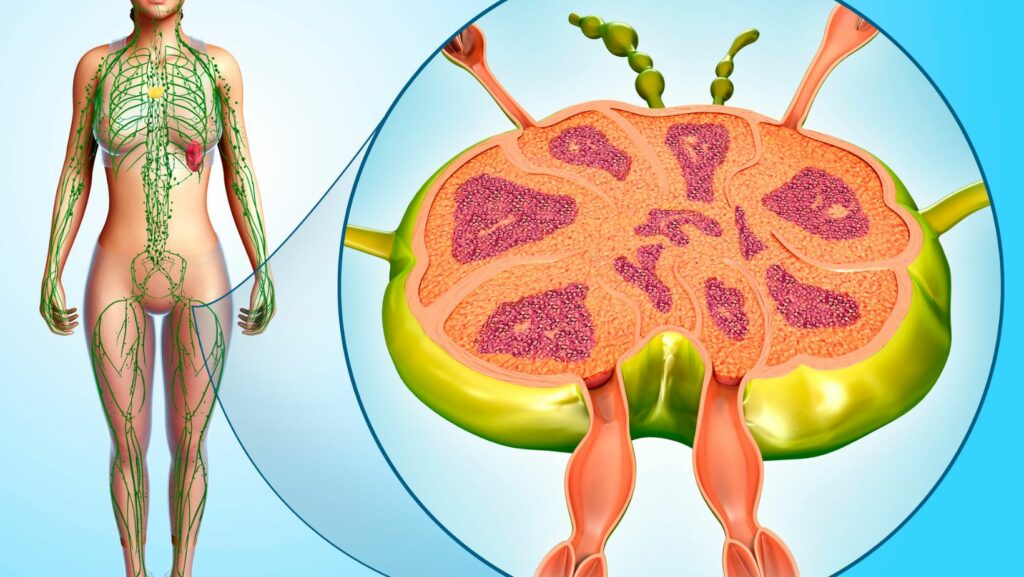
The lymphatic system is a complex network of vessels, organs, and lymph nodes that work together to defend our bodies against infections and diseases. It acts as a drainage system, carrying excess fluid called lymph from tissues back into the bloodstream. Moreover, it houses various immune cells that help identify and eliminate harmful pathogens.
Understanding the different components of the lymphatic system can be perplexing at first, but with proper labeling, we can gain clarity on its functions. From lymph nodes to lymphatic vessels and spleen to tonsils, each part has its own unique purpose within this intricate network. Join me as we explore these features in detail and unravel the mysteries of this remarkable bodily system.
Overview of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a vital network of tissues, organs, and vessels that work together to support our immune system and maintain fluid balance in the body. It plays a significant role in protecting us from infections, removing waste products, and transporting fats from the digestive system.
Key Components
- Lymph Nodes: These small bean-shaped structures filter lymph fluid and contain immune cells that help fight off harmful substances.
- Lymph Vessels: Similar to blood vessels, lymphatic vessels carry lymph fluid throughout the body. They collect excess fluid from tissues and return it to the bloodstream.
- Spleen: The largest organ in the lymphatic system, the spleen filters blood, removes old or damaged red blood cells, and produces white blood cells.
- Thymus: Located behind the breastbone, this gland is essential for proper development and functioning of T-cells, which are crucial for immune responses.
- Bone Marrow: Found within bones, bone marrow produces different types of blood cells including white blood cells involved in immunity.
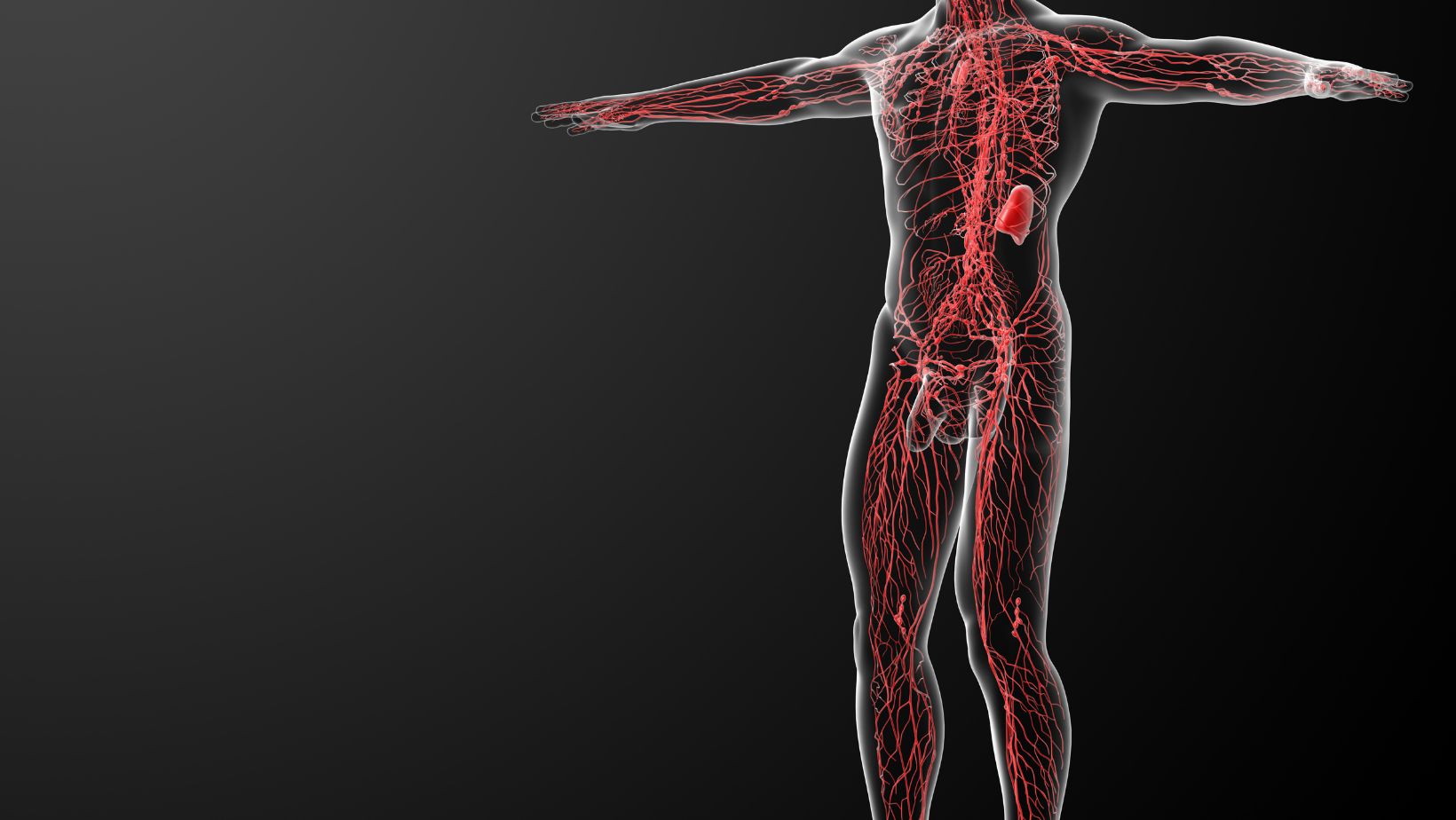
Functions of the Lymphatic System
- Immune Defense: The lymphatic system acts as a defense mechanism against invading pathogens such as bacteria or viruses. It helps identify foreign substances by carrying them to lymph nodes where specialized immune cells can eliminate them effectively.
- Fluid Balance: Excess interstitial fluid (fluid between cells) is collected by lymphatic vessels and returned to circulation. This process prevents swelling or edema in tissues.
- Fat Absorption: Specialized lacteals within the small intestine’s lining absorb dietary fats into lymph vessels called chyle. Chyle eventually reaches veins near the heart where fats are transported throughout the body.
Disorders While an efficient functioning lymphatic system is crucial for overall health, certain conditions can affect its performance:
- Lymphedema: A condition characterized by swelling, usually in the arms or legs, due to a blockage or damage in lymphatic vessels. It can result from surgery, radiation therapy, infection, or genetic abnormalities.
- Lymphoma: A type of cancer that affects lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and can occur in the lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and other parts of the body.
- Infections: The lymphatic system can become infected by bacteria or viruses, leading to conditions such as tonsillitis or lymphadenitis.
Understanding the intricacies of the lymphatic system is essential for comprehending its vital role in our overall well-being. From immune defense to fluid balance and fat absorption, this intricate network serves as a remarkable guardian within our bodies. So next time you come across swollen glands during an illness or notice how your body recovers from infections remarkably well, remember to appreciate the wonders of your hard-working lymphatic system.





